AI & Creativity: A Guide to 2025–2026 Trends
Artificial intelligence is becoming an essential creative tool — one that expands the designer’s capabilities rather than replacing them. The “human vs. AI” debate is fading, giving way to a symbiotic relationship: generative models accelerate routine tasks and spark new ideas, while the final creative touch and emotional depth remain in human hands.
AI enhances creativity but doesn’t substitute for it. It lacks emotional empathy because it has never lived a human life, attended a client meeting, or sensed the subtle nuances hidden within a brief. For now, it cannot perceive the faint shifts in body language that humans intuitively notice.
AI as a designer’s partner, not a replacement
Authenticity, texture, and the beauty of imperfection in visuals
After a wave of perfect digital AI images, there’s a growing demand for more realistic and tactile visuals. Designers are intentionally adding “imperfections”: grain, hand-drawn strokes, complex textures to make visuals feel alive and tangible. Minor flaws and irregularities make content warmer, more relatable, and emotionally resonant. Even in logo and identity design, it’s become clear that a fully AI-generated brand can feel soulless unless human intuition and empathy are woven into the process.
In digital design, tactile aesthetics is on the rise — when it visually appears three-dimensional, as if you could touch it: grainy effects, depth, material imitation.
Generative video and animation in creative work
The year 2025 marks a breakthrough in AI video generation: new models can now produce short clips with increasingly high quality. OpenAI has released Sora 2, a model capable of generating cinematic video from text prompts — complete with realistic motion physics and synchronized sound. Sora 2 understands cause and effect: when a ball misses the basket, it bounces away instead of “teleporting” into the hoop.
Meanwhile, startups are advancing tools like Runway, improving frame clarity, motion stability, and control in generated videos.
AI animation has become a reality, with new tools that can bring static images to life based on text descriptions. This trend opens up fresh storytelling formats for brands: from AI-generated commercials to dynamic animated visuals for social media. Neural networks are already being used for rapid storyboarding and campaign previsualization, accelerating the creative workflow. Studios like Lionsgate (known for John Wick and The Hunger Games) partner with Runway to integrate generative AI into content production.
AI-powered ad generation also cuts costs and timelines: PUMA, Popeyes, and Coca-Cola have already launched such projects.
Surrealism and the rise of new creative worlds
Generative AI opens an extraordinary space for imagination, giving brands limitless room to experiment. The emerging trend centers on campaigns that build entire imaginary universes — concepts that would once have been too costly or complex to produce. The fusion of real and digital blurs the boundaries between what’s possible and what’s imagined.
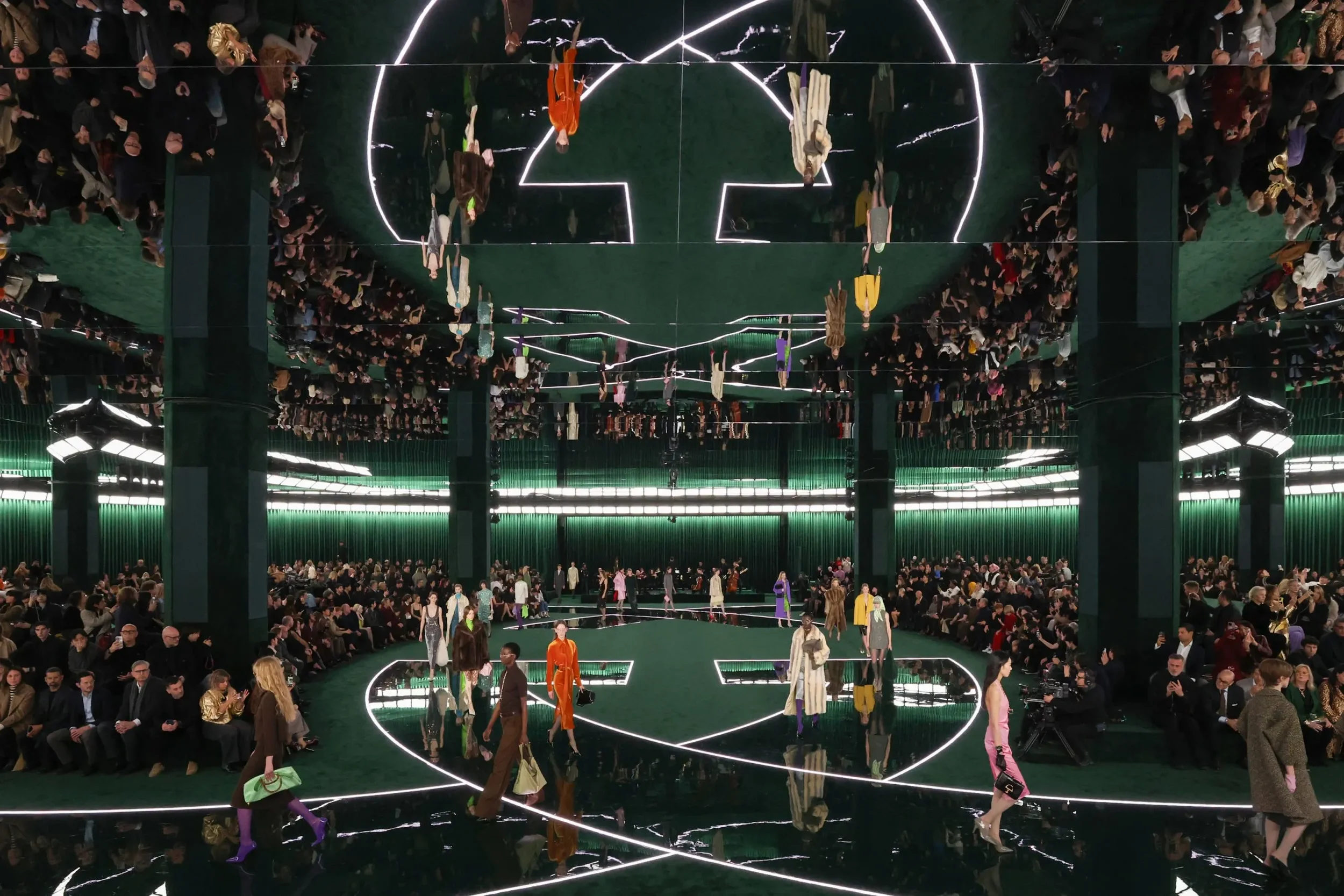
Milan Fashion Week: Gucci FW25Thalie Paris’s groundbreaking AI-generated virtual campaignFor example, Burberry has developed immersive fitting rooms, while Valentino’s Essentials campaign represents a groundbreaking fusion of fashion and artificial intelligence. AI was used to craft stunning visual compositions that highlight the distinctive interplay between human creativity and machine intelligence.
Antitrends and common mistakes
As generative networks evolve, consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the distinctive synthetic look of some AI-generated visuals. Today, overly smooth, lifelessly perfect renders can trigger rejection. Highly polished images that lack texture and organic details are perceived as artificial, repetitive, and soulless.
The “plastic” digital aesthetic
This impersonal digital gloss only highlights the machine-made nature of the image, which can weaken audience connection and reduce brand affinity. That’s why it’s crucial to incorporate a human touch into AI-generated art: subtle imperfections, material imitations, and warmth in color. Paradoxically, AI can not only boost sales — it can also diminish them.
AI instead of humans
Another antitrend is viewing AI as a way to replace human involvement in creative work. AI lacks lived experience, empathy, and the ability to grasp subtle cultural contexts.
Emotional connections with an audience are built on human stories and values. Branding and advertising are, above all, about feelings and meaning, which AI simply does not possess.
In the August issue of Vogue US, a GUESS ad spread featuring fully AI-generated models received strong backlash. The magazine is traditionally associated with real models: their personalities, individuality, and human depth. The public criticized both Guess and Vogue for promoting unrealistic beauty standards and depriving real models and photographers of paid opportunities. Many social media users guessed that women would now begin comparing themselves not even to people, but to robots.
When P&G launched a CGI avatar to promote skincare products, the response was similarly cold. For many, the campaign felt eerie and insincere: a brand meant to embody naturalness presented a plastic, artificial face instead.
Mass content without meaning
*Example of poor AI usage. Image from open sources.
*Example of poor AI usage. Image from open sources.
*Example of poor AI usage. Image from open sources.
Amid the hype around AI, there’s a growing temptation to generate more visuals and text simply because it’s easy. But content for the sake of content has already become a clear anti-trend. Audiences are already beginning to recognize images thoughtlessly created by AI: they are characterized by cliched plots, repetitive styles, and facelessness. Oversaturating users with AI videos or artworks can reduce a brand's value. AI should be applied purposefully and in moderation, guided by a brand’s overarching strategy.
*Example of poor AI usage. Image from open sources.
According to the Sprout Social Index, one in three users believes that when a brand jumps on a viral trend just for reach, it comes across as awkward and inauthentic. Building a strong social presence requires understanding what truly matters to the community and only then using AI to enhance that strategy. Brand identity, audience characteristics, and context all determine what kind of content (and how much of it) should be created with AI.
Key AI tools
Video generation
AI video generation is a rapidly developing field. The Runway ML platform became the first commercial solution for creating videos from text descriptions in 2023, and even in 2025 this tool remains highly popular among brands.
Runway makes it possible to generate short clips from scratch and to transform existing videos according to a specified style. Major production studios are also showing interest in it, recognizing the potential for automating parts of the filming process, for example, for storyboards, scene previsualization, and even some visual effects.
In 2025, OpenAI released its flagship product — Sora 2. It is a powerful model that creates HD videos with sound. Sora 2 can follow complex scripts with multiple shots and maintain narrative logic while simultaneously generating an audio track (speech and effects) that matches the video. The Cameos mode allows any person, animal, or object to be placed into an AI-generated environment with an accurate appearance and voice. For now, the length of generated videos is limited to several dozen seconds.
There are also models capable of turning static images into short animated GIFs or videos. Some tools work with 3D: for example, Luma AI offers Dream Machine, which can transform a text script and sketches into realistic 3D scenes. This tool is also used for video creation.
Another tool is Pika Labs, focused on creators in the digital environment. Pika can create 4–10-second clips from text (perfect for TikTok or Reels) and is appreciated for its simplicity. Using the Ingredients feature, users can upload an image of a character or object, and the algorithm will embed it into the generated video while maintaining the appearance and style of the original.
This approach solves the issue of visual consistency, for example, a brand can use its virtual ambassador across multiple scenes, confident that the character will look the same in every video.
In addition to photo and video generation, there is a whole layer of AI tools for creative design. For instance, services like Canva and Visme have integrated GPT-based assistants for generating presentations, landing pages, and branded content. It is enough to provide a short description and upload brand guidelines, and the AI will offer ready-made templates in your style.
Other platforms for working with video and characters are also developing actively. Heygen allows creating videos featuring a specific face or character, including voice and speech synchronization. Pika is used to produce viral short videos with dialogues and everyday scenes, especially popular on TikTok and Reels. Pictory is applied for automated video editing and adaptation for social media. Veo from Google is used to create AI films — the neural network can remember faces and reproduce the same character in different scenes, building a coherent visual story.
Image generation
In the field of visual creation, text-to-image models dominate, capable of producing high-quality visuals in seconds and in virtually any style. The most in-demand tools remain Midjourney and OpenAI’s DALL·E 3, each having established its own niche. Midjourney excels when beauty, atmosphere, artistry, and a strong aesthetic identity are the priorities. It’s particularly powerful for concept art, fantasy worlds, fashion visuals, and cinematic or surreal scenes that require cohesion and mood. Even with minimal prompting, the results tend to look expressive and polished.
DALL·E 3 is valued for its precision and compositional accuracy. It rarely over-interprets prompts and performs significantly better when generating text within images. Another advantage is its integration with ChatGPT, which simplifies and speeds up the creative workflow.
Both tools are widely used in brand design: from rapid prototyping (sketches, storyboards) to final materials (background scenes, distinctive visual objects).
Models such as Stable Diffusion are also gaining traction, allowing teams to fine-tune them for brand-specific aesthetics and generate content aligned with a company’s visual DNA. Interest is also growing in other solutions like Sora, Leonardo, Meitu (a mobile app with built-in creative templates), Adobe Firefly, and Google’s Veo 3, all known for their intuitive interfaces and ability to generate high-quality visuals even in free modes.